Laser Safety
Laser Safety Overview
The 2V03 Underbody Floor Skin Cell features Laser Cutting Booths to perform laser cutting operations. The laser cutting booths are designed to protect persons from exposure to the Class 4 laser direct or scattered radiation. Exposure to the laser bear, even when reflected off of other surfaces, can cause permanent eye injury and blindness. To protect yourself from exposure to the laser beam, the following laser safety precautions must be taken:
Lasers are designed to deliver a large amount of energy to a very small area. In cutting operations, this energy can heat metals quickly to very hight temperatures. Much of the radiation that strikes the work piece is reflected into the environment, creating hazards. Some laser light used for cutting may be infrared, and therefore, the beam may be invisible.
Lasers can cause severe skin and eye injuries, resulting in permanent vision loss. Studies of laser accidents have shown several contributing factors. The following are common causes of laser injuries:
- Inadequate training of laser personnel
- Alignment performed without adequate procedures
- Failure to block beams or stray reflections
- Failure to wear eye protection in hazardous situations
- Failure to follow approved standard operating procedures or safe work practices
Laser Hazards
Laser light poses safety hazards for all laser users and persons near the laser equipment. Each person must be aware of the hazards involved in operating the laser.
Local, State, or Federal requirements as well as facility or building requirements may also apply for using the laser or laser system.
The laser processing head must ONLY be operated if all protection equipment and safety-related devices are fully functional!
Laser Cutting Concerns
Electrical: Most laser utilize high voltages that can be lethal.
Radiation: Both visible and invisible light radiation is produced when cutting. Due to the interaction with the work piece, high levels of hazardous blue light and ultraviolet radiation (secondary radiation) are produced. This light radiation is often reflected from the work piece into the work area. Radiation from these processes can seriously burn eyes and skin quickly, causing permanent damage.
Laser and Eyes: Acute exposure of the eye to lasers of certain wavelengths and power can cause corneal or retinal burns (or both). Chronic exposure to excessive levels may cause corneal, lenticular opacities (cataracts), or retinal injury. Lasers operate in the ultraviolet, visible, and infrared.
Laser light in the visible to near infrared spectrum (i.e. 400 to 1400 nm) can cause damage to the retina resulting in scotoma (blind spot in the fovea). This wave band is also known as the "retinal hazard region."
Laser light in the ultraviolet (290 to 400 nm) or far infrared (1400 to 10,600 nm) spectrum can cause damage to the cornea and / or to the lens. Retinal damage may be associated with an audible "pop" at the time of exposure. Visual disorientation due to retinal damage may not be apparent to the operator until considerable thermal damage has occurred.
Eye Protection: In addition to the primary hazard of the laser beam, there may be a considerable eye hazard from hight levels of secondary radiation. Ultraviolet light may be leaked into the workplace. Thus, the eyewear should provide primary beam protection, secondary radiation protection, and ultraviolet protection.
Laser Protective eye wear is available and worn by all personnel within the Normal Hazard Zone (NZH) of Class 3b and Class 4 Lasers where the exposures above the Maximum Permissible Exposure (MPE) can occur. Eye wear must be labeled with both the optical density (protective factor) and wavelength(s) for which the protection is afforded. This is especially important in areas where multiple lasers are housed. The protective eye wear must be compatible with the manufacturer's specifications for the laser system in use to ensure that the eye wear is suitable. Laser protective eye wear shall be inspected for damage prior to use.
Skin Hazards: High power lasers can cause skin burns. Exposure of the skin to high power laser beams (1 or more watts) can cause burns. At the under five watt level, the heat from the laser beam will cause a flinch reaction before any serious damage occurs. The sensation is similar to touching any hot object. You tend to pull your hand away or drop it before any major damage occurs. With higher power lasers, a burn could occur even though a flinch reaction may rapidly pull the affected skin out of the beam. These burns can be quite painful as the affected skin can be cooked, and forms a hard lesion that takes considerable time to heal. Ultraviolet laser wavelengths may also lead to skin cancer.
Fire: Since the laser system produces a small spot size with high energy, the hazard of fire is present if the beam hits flammable material. Keep all flammables away from the cutting area. Be sure to cover and protect anything flammable in the area since reflected radiation could start fires in unexpected places. Protect the work area!
Safety Needs:
- All integration and use of any laser system should be monitored by a qualified laser safety representative. All laser cutting installations are required to have a Laser Safety Officer (LSO).
- The LSO is responsible for personnel protection, laser cell class conformance and enforcement of all laser safety regulations.
- The LSO is responsible for training the laser equipment personnel (at least once a year) in the risks associated with laser radiation and appropriate safety measures.
- Due to these inherent risks, a qualified safety representative should be present to ensure a safe working environment.
- Fully read and understand all laser safety information contained n this section as well as safety instructions found in the OEM documentation provided with this equipment. The best source of safety information is provided in the instruction manual from the manufacturer of the laser equipment. Always read, understand, and follow the manufacturer's recommended safety procedures.
Lockout any applicable energy sources before performing any work within the gated area.
When a safety gate has been opened, it can be locked out by placing the lockout device through the sliding handle to prevent the handle pin from sliding back into the receiver. If more than one person is to enter the cell, each person must place a locking device on the gate handle. Lock out the safety gate BEFORE entering into the cell.
Laser Cutting Booth Safety Features
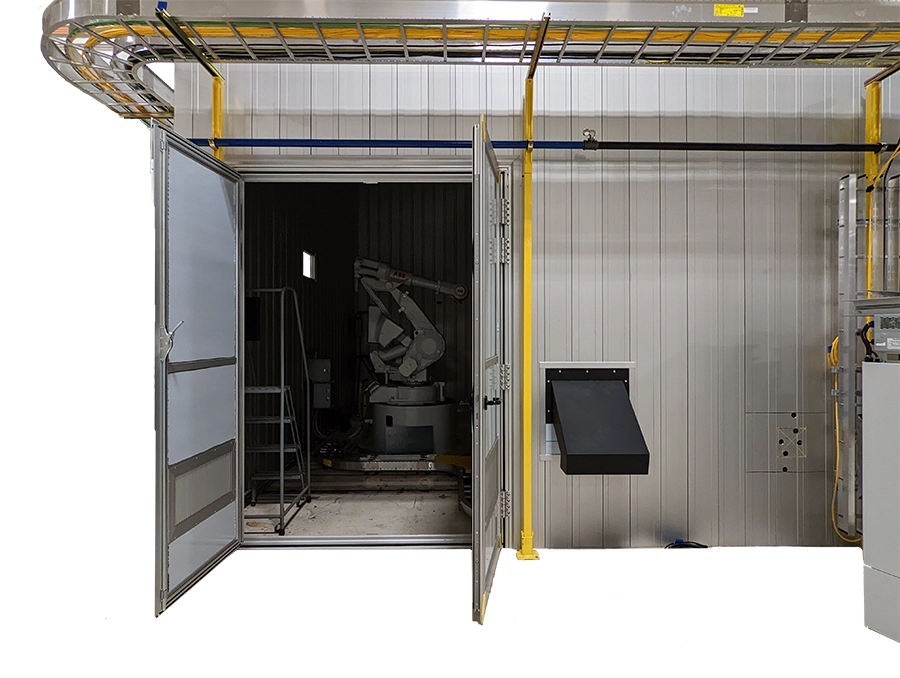
The Cutting Booth refers to the enclosed, light-tight room where the robotic welding / cutting operations take place. The cutting booth, when fully closed and interlocked, provides light-tight protection, and prevents harmful laser emissions from leaving the booth.
The laser cutting booth is designed to be light-tight to protect persons from exposure from the Class 4 laser's direct or scattered radiation. Exposure to the laser beam, even when reflected off of other surfaces, can cause permanent eye injury and blindness. The Laser Cutting Booth is highlighted in blue on the right side of the screen.
Interlocked Safety Door
There are two (2) interlocked safety doors to provide access to the interior of the Laser Cutting Booth. The door incorporates a safety switch along with a safety relay control device to monitor the position of the door’s opened and closed position. If personnel open the access door to the cutting booth while the laser is operational, the interlocks (switch) will send a signal to the control system to immediately stop the laser and all robot motion.
The safety gate switch has provisions for applying a multiple lockout device (scissor lock) to the door handle when all motion has stopped. Persons working within the cell will follow all Lockout / Tagout (LOTO) procedures and apply their personal padlock to the multiple locking device.
Door Seals
The Door Seals are located on the door and door frame. the door seals ensure the reflected light and scattered radiation is contained within the booth. Periodic inspection for damage to the seal is required.
Automatic Slide Window
The Laser Cutting Booth features an automatic sliding window to allow the material handling robot to place the part into the laser hold turntable fixture. Once in position and the material handler robot returns to the home position, the automatic slide window will lower into the closed position to protect personnel from the laser radiation and laser cutting process. After the process is completed and all hazardous emissions and radiation is removed from the booth, the automatic slide window will raise and allow for the material handler robot to remove the part from the fixture.